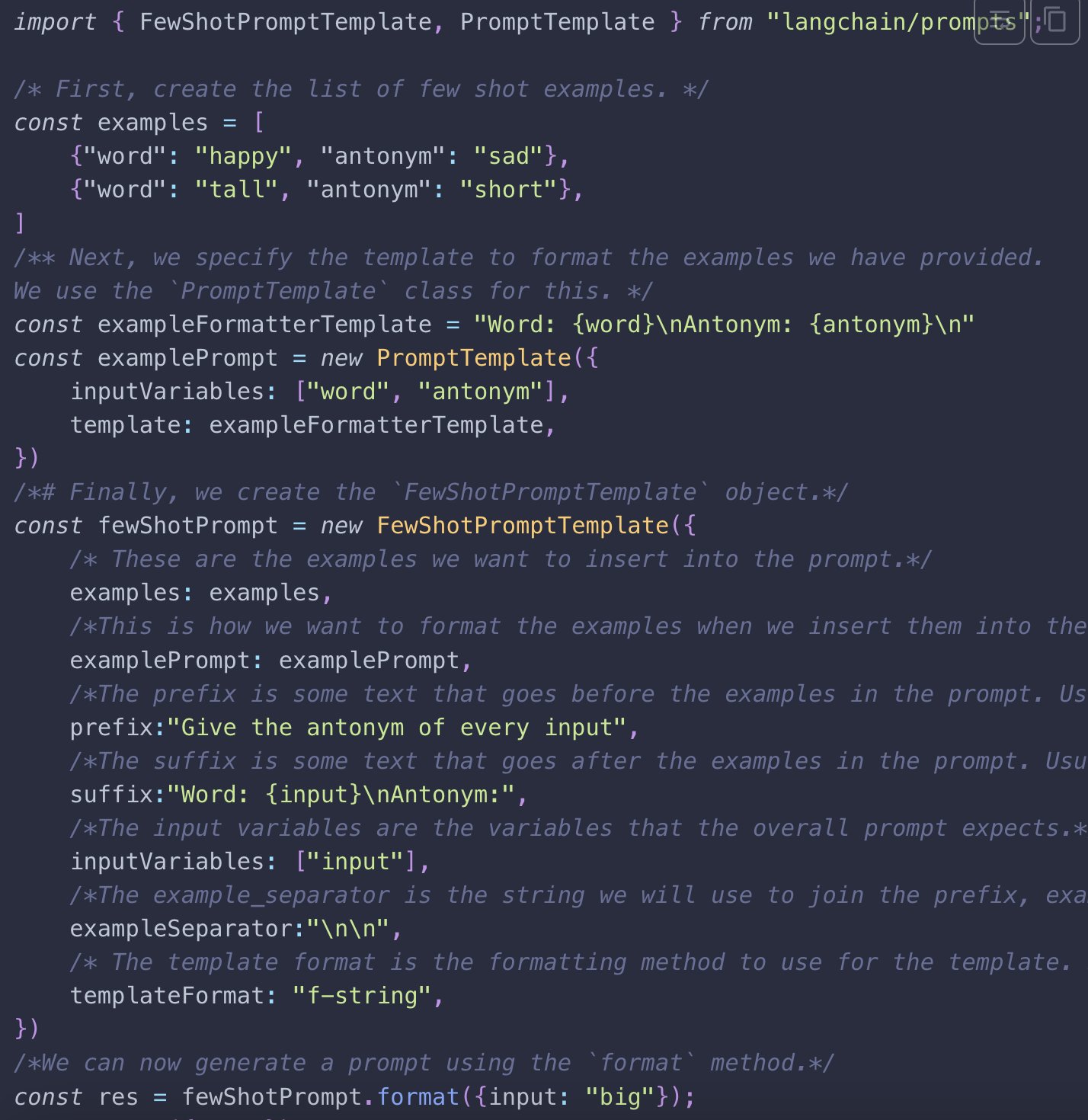
Langchain Prompt Template The Pipe In Variable
Langchain Prompt Template The Pipe In Variable - We'll walk through a common pattern in langchain: Formats the prompt template with the provided values. In this tutorial, we will explore methods for creating prompttemplate objects, applying partial variables, managing templates through yaml files, and leveraging advanced tools like. Memories can be created in two ways: A pipelineprompt consists of two main parts: It accepts a set of parameters from the user that can be used to generate a prompt.
Context and question are placeholders that are set when the llm agent is run with an input. Includes methods for formatting these prompts, extracting required input values, and handling. Each prompttemplate will be formatted and then passed to future prompt templates. Get the variables from a mustache template. This can be useful when you want to reuse.
Prompts.string.validate_jinja2 (template,.) validate that the input variables are valid for the template. From langchain.chains import sequentialchain from langchain.prompts import prompttemplate # ステップ1: Context and question are placeholders that are set when the llm agent is run with an input. Each prompttemplate will be formatted and then passed to future prompt templates. A prompt template consists of a string template.
Includes methods for formatting these prompts, extracting required input values, and handling. This can be useful when you want to reuse parts of prompts. Invokes the prompt template with the given input and options. Prompt template for composing multiple prompt templates together. Prompt template for a language model.
Includes methods for formatting these prompts, extracting required input values, and handling. You can learn about langchain runnable interface, langserve, langgraph, and a few other terminologies mentioned by following langchain documentation. It accepts a set of parameters from the user that can be used to generate a prompt for a language. Prompt templates take as input an object, where each.
A pipelineprompt consists of two main parts: Context and question are placeholders that are set when the llm agent is run with an input. Prompt templates take as input an object, where each key represents a variable in the prompt template to fill in. Memories can be created in two ways: This can be useful when you want to reuse.
This is why they are specified as input_variables when the prompttemplate instance. Prompt templates take as input an object, where each key represents a variable in the prompt template to fill in. Invokes the prompt template with the given input and options. Pipelineprompttemplate ( * , input_variables : Langchain integrates with various apis to enable tracing and embedding generation, which.
Langchain Prompt Template The Pipe In Variable - This promptvalue can be passed. Pipelineprompttemplate ( * , input_variables : It accepts a set of parameters from the user that can be used to generate a prompt. We'll walk through a common pattern in langchain: Prompt template for a language model. In the next section, we will explore the different ways.
Using a prompt template to format input into a chat model, and finally converting the chat message output into a string with an output parser. This can be useful when you want to reuse parts of prompts. A prompt template consists of a string template. List [ str ] , output_parser : You can learn about langchain runnable interface, langserve, langgraph, and a few other terminologies mentioned by following langchain documentation.
In This Tutorial, We Will Explore Methods For Creating Prompttemplate Objects, Applying Partial Variables, Managing Templates Through Yaml Files, And Leveraging Advanced Tools Like.
Context and question are placeholders that are set when the llm agent is run with an input. Invokes the prompt template with the given input and options. 👉 in the hot path (this guide): Memories can be created in two ways:
Prompt Template For A Language Model.
For example, you can invoke a prompt template with prompt variables and retrieve the generated prompt as a string or a list of messages. This is why they are specified as input_variables when the prompttemplate instance. List [ str ] , output_parser : In the next section, we will explore the different ways.
This Can Be Useful When You Want To Reuse.
We'll walk through a common pattern in langchain: Prompt template for a language model. Prompt templates take as input an object, where each key represents a variable in the prompt template to fill in. From langchain.chains import sequentialchain from langchain.prompts import prompttemplate # ステップ1:
Prompt Template For Composing Multiple Prompt Templates Together.
A prompt template consists of a string template. It accepts a set of parameters from the user that can be used to generate a prompt. Prompts.string.validate_jinja2 (template,.) validate that the input variables are valid for the template. Prompt templates output a promptvalue.